When using generative AI for structured data collection, the language of the prompt can make a real difference. In our test with Hungarian population statistics, both Claude Opus 4.1 and Sonnet 4 produced accurate outputs when prompted in Hungarian – but with an English prompt, Sonnet 4 generated rounded figures and slight discrepancies. This shows that for country-specific or non-English data, it is worth testing prompts in the local language to ensure reliability.
Prompt
In English:
Please collect Hungary's official annual population data broken down by county, including Budapest, from 2015 to 2025. Collect the data in a downloadable Excel file with a clear structure, indicating the annual values and the changes from year to year.
In Hungarian:
Kérlek, gyűjtsd össze Magyarország hivatalos éves népességi adatait megyénkénti bontásban, Budapestet is beleértve, 2015-től 2025-ig. Az adatokat egy letölthető Excel fájlba gyűjtsd össze, világos szerkezettel, az éves értékek és az évről évre bekövetkező változások feltüntetésével.
Output
Claude Opus 4.1:
One particularly interesting feature of Claude Opus 4.1 was its ability to organise the task by designating subagents. Instead of tackling the entire request in one go, the model broke the process down into distinct phases: one subagent focused on recent data (2020–2025), another on historical years (2015–2019), and a third on verifying completeness and cross-referencing sources.
During the research process, Opus 4.1 also pulled in some unexpected references – for instance, a link to a Kenyan population report briefly appeared among the consulted sources. However, this did not interfere with the outcome: the final table was compiled from the correct KSH dataset and contained the appropriate Hungarian figures.
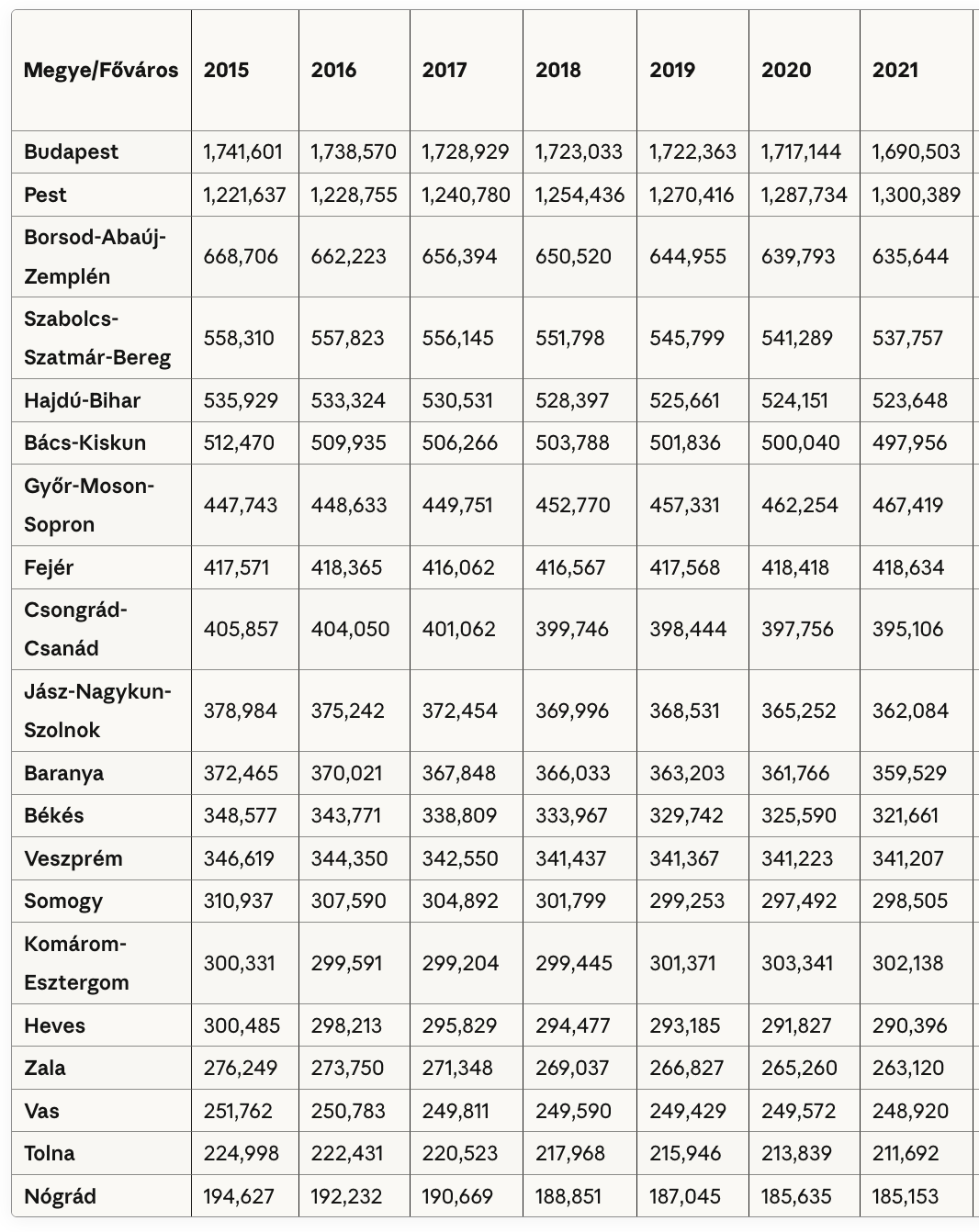
Claude Sonnet 4:
When prompted in Hungarian, Sonnet 4 successfully compiled all the requested population data for Hungary by county, including Budapest, across the examined years. The tables were clear, structured, and contained accurate values consistent with the official KSH figures.
However, when the same task was run with an English-language prompt, the output showed some irregularities. While the majority of values were correct, the model occasionally introduced rounding – sometimes upwards, sometimes downwards – to the nearest ten or hundred. This behaviour appeared entirely ad hoc, as most of the dataset remained precise. The most visible discrepancies occurred in counties such as Zala and Heves, but scattered rounding could also be observed elsewhere.
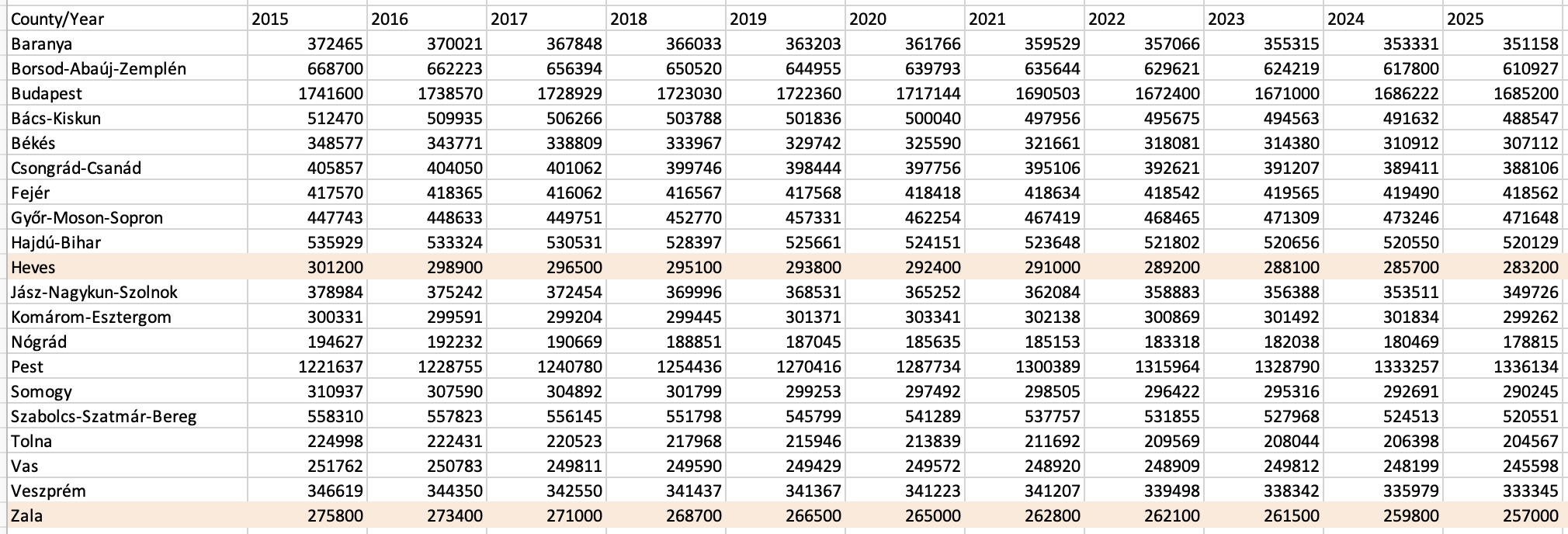
Recommendations
Our comparison highlights that prompt language can influence the consistency of AI-assisted data collection. While both Claude Opus 4.1 and Sonnet 4 returned correct Hungarian population data when asked in Hungarian, the English prompt led Sonnet 4 to introduce ad hoc rounding in some counties. For tasks involving official or country-specific statistics, it is therefore advisable to experiment with local-language prompts and always validate the outputs against the original sources.
The authors used Claude Opus 4.1 [Anthropic (2025) Claude Opus 4.1 (accessed on 27 September 2025), Large language model (LLM), available at: https://www.anthropic.com] to generate the output.





