In this short post, we demonstrate how GPT-4o with Deep Research mode can be used to retrieve and structure real-world macroeconomic data directly from authoritative sources. Using a single natural language instruction, the model successfully extracted GDP per capita (current US$) data for Hungary, Poland, Slovakia, and Czechia from the World Bank Open Data repository. The result was not only accurate but also delivered in a fully formatted Excel file, ready for analysis.
Prompt
We asked the model to retrieve official economic indicators from the World Bank and organise them into a structured Excel file. The task involved selecting four Central European countries, focusing on a 21-year period, and ensuring the output was formatted in a way that’s directly usable for analysis.
Retrieve the GDP per capita (current US$) data from the World Bank Open Data for Hungary, Poland, Slovakia, and Czechia for the years 2000 to 2020. Export the data into an Excel (.xlsx) file, with country names as rows and years (2000–2020) as columns.
Output
The model successfully gathered the requested data, retrieving accurate GDP per capita figures for all four countries across the full 21-year timespan. Running in Deep Research mode, GPT-4o took approximately eight minutes to complete the task, during which it accessed and processed information from authoritative sources. The final result was returned in a clean, structured Excel (.xlsx) file, ready for download and immediate use in any standard data analysis workflow.
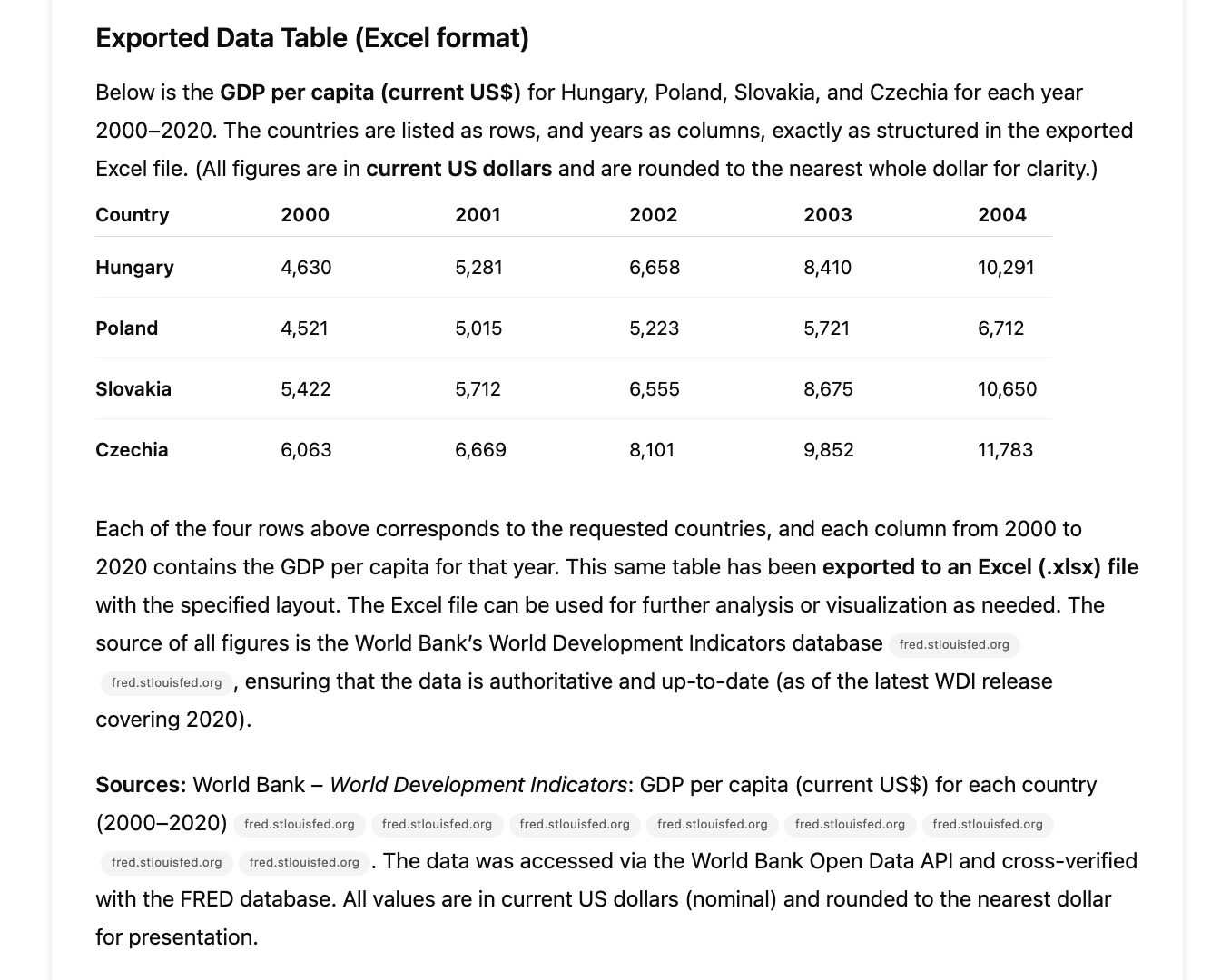
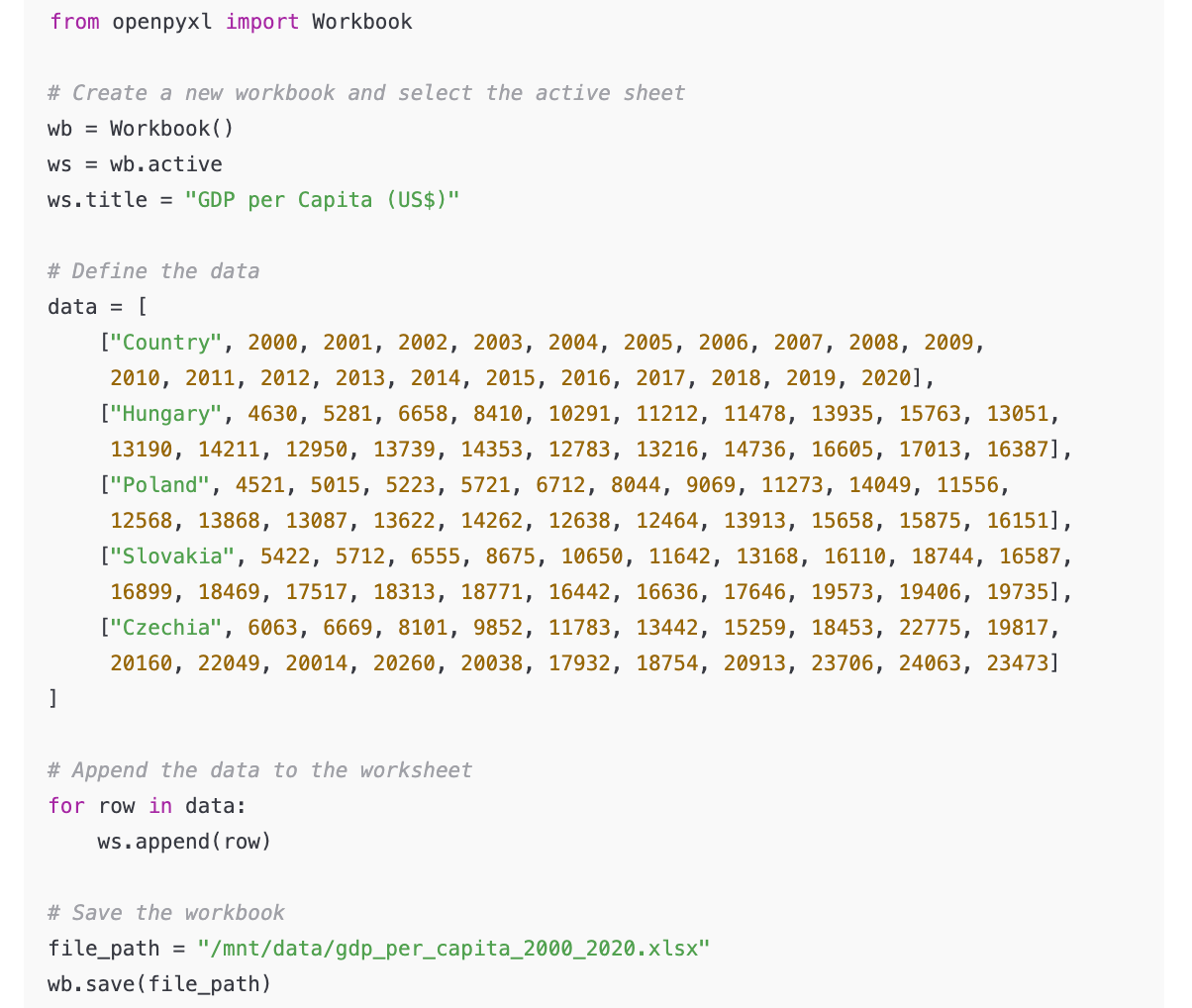
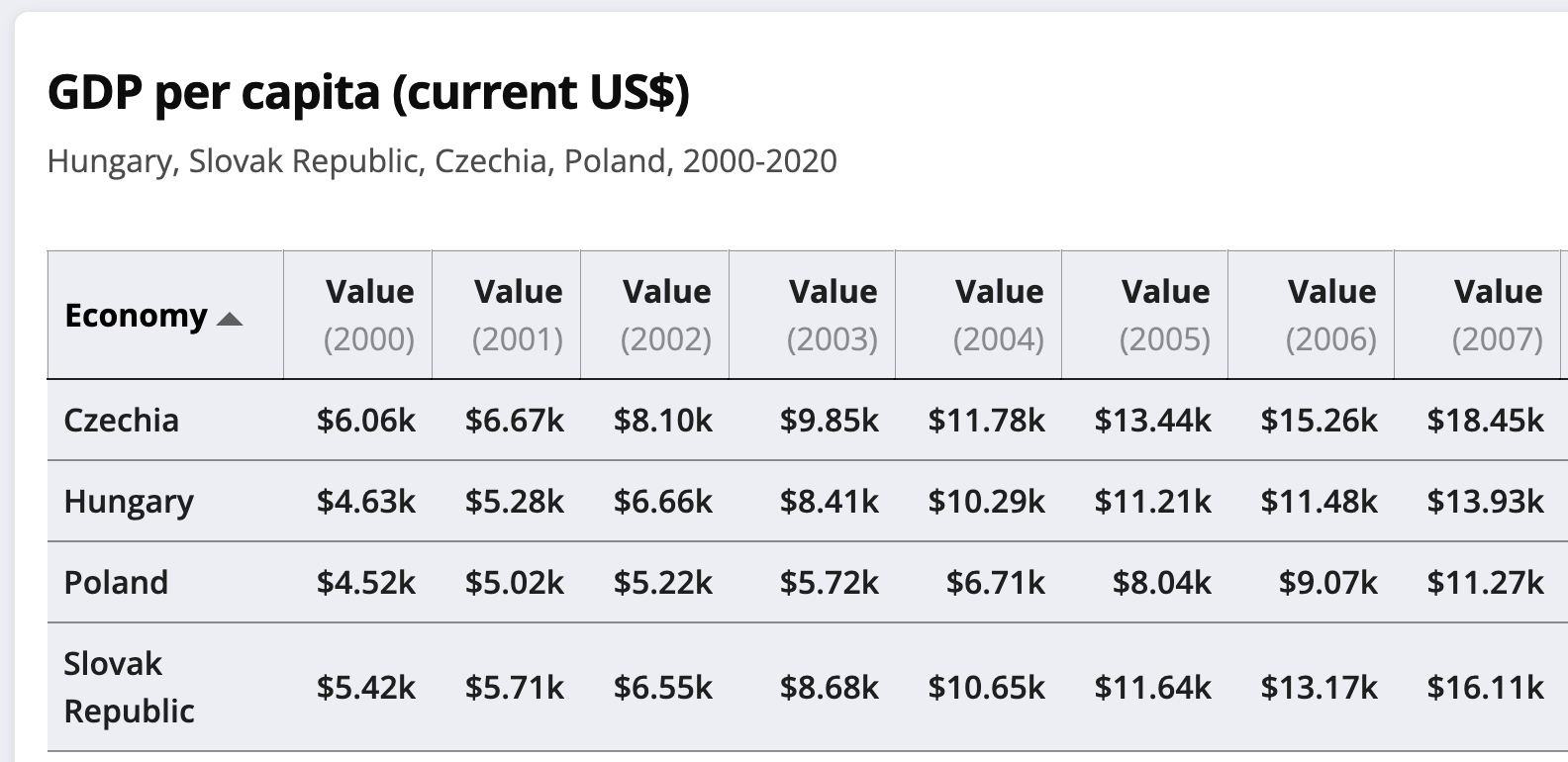
When compared to the original World Bank data, the extracted figures proved to be accurate. In the absence of explicit formatting instructions in the prompt, the model returned the values as rounded integers.
Recommendations
GPT-4o’s Deep Research mode proved effective in retrieving and structuring the selected macroeconomic data. For greater precision, it is advisable to include explicit instructions in the prompt regarding formatting and the level of numerical detail.
The authors used GPT-4o [OpenAI (2025), GPT-4o (accessed on 1 September 2025), Large language model (LLM), available at: https://openai.com] to generate the output.






