As AI image generation tools become increasingly sophisticated, the ability to distinguish between AI-generated and authentic photographs has emerged as a critical challenge. Platforms like Winston.AI and AI or Not claim to address this need by detecting synthetic imagery with high accuracy. But how well do these detection systems perform when tested systematically? In this post, we evaluate both platforms using a controlled set of AI-generated and genuine images to assess their reliability in real-world scenarios.
Tool Overview
We evaluated two prominent tools for detecting AI-generated imagery:
Winston AI – Best known for their AI-text detection –which we have not presented in a systematic test yet – Winston AI also offers an image-analysis feature. It returns a confidence score to indicate how strongly the system believes the image is likely AI-generated vs. authentic.
AI or Not – A purpose-built image detection tool focused on identifying synthetic or AI-altered visuals. It is positioned as a straightforward way to screen images and flag content that may warrant closer scrutiny.
Both tools are marketed as accessible, low-friction options for researchers, educators, content moderators, and others who need to assess image authenticity amid rapidly improving generative image models.
Testing Approach
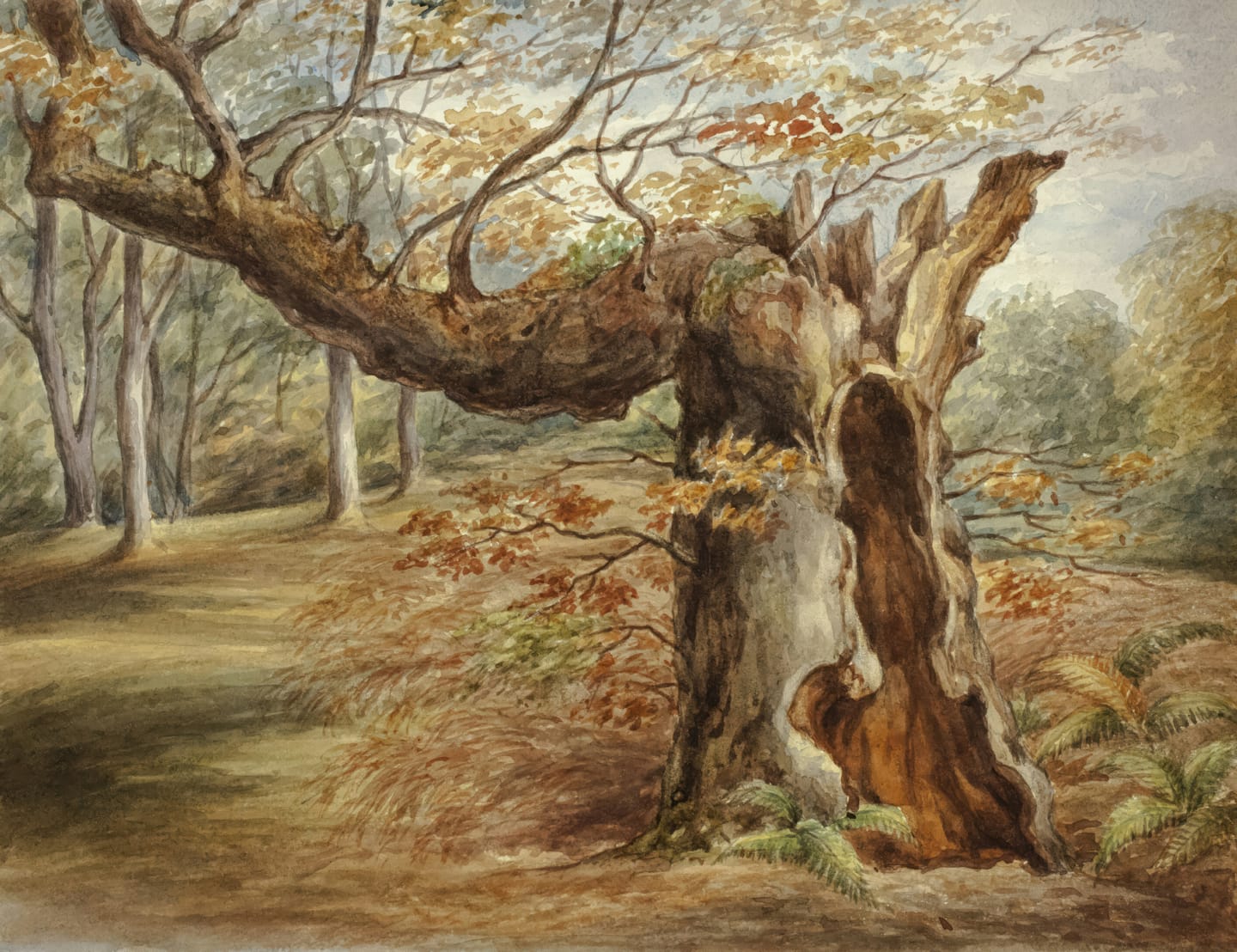
To evaluate the detection capabilities of both platforms, we created a controlled test set consisting of three AI-generated images and one authentic photograph, all depicting similar subject matter: a solitary oak tree in a meadow.
Image Generation
We generated three images using different AI systems, each with the same standardised prompt:
Generate a photorealistic image of a single mature oak tree standing alone in the middle of a meadow, natural midday lighting, wide shot, realistic colors and detail, no people, no buildings, no animals, no text.
The AI models we used and their corresponding images were:
Gemini 3 (Nano Banana Pro)
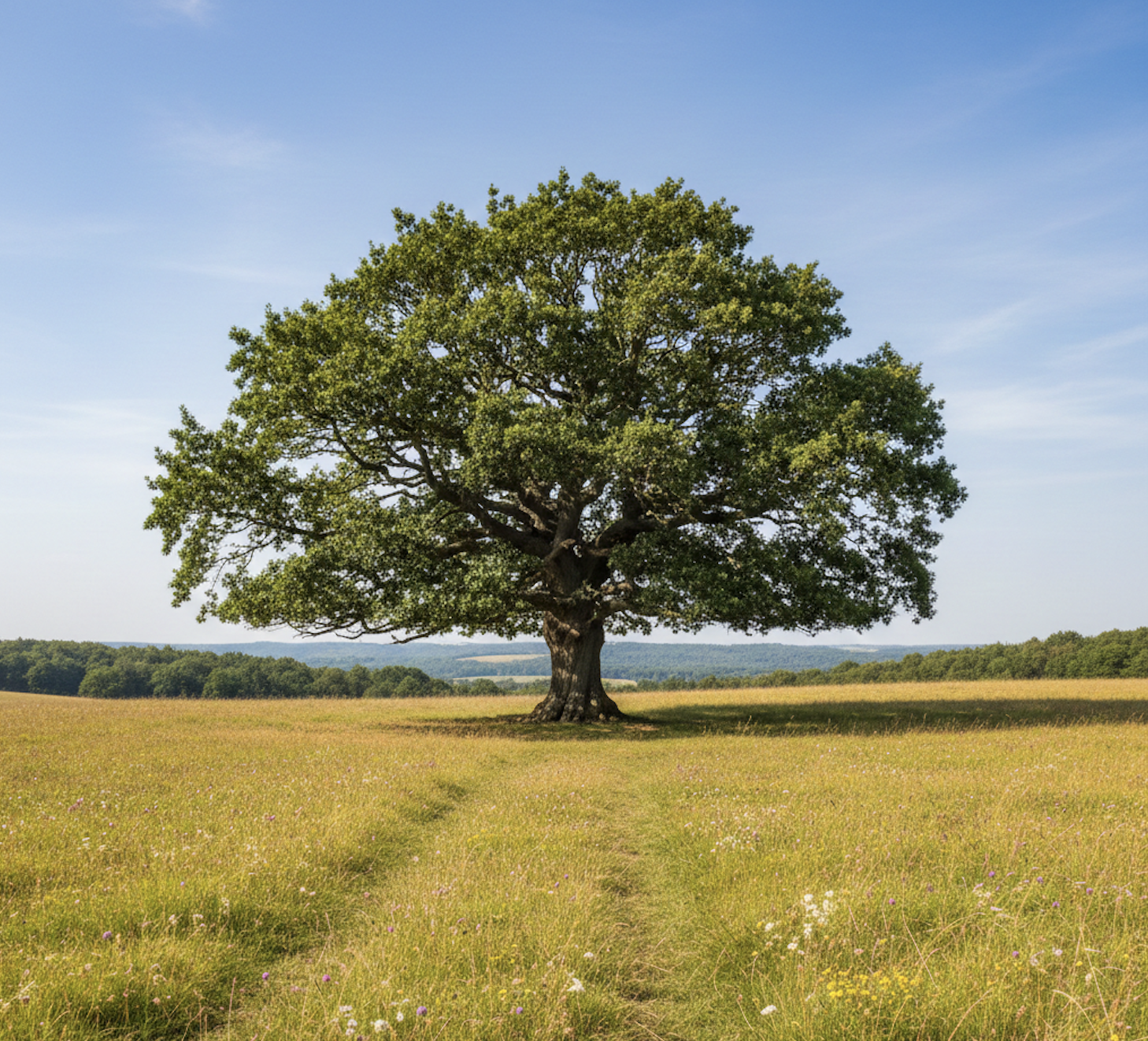

GPT 5.2 (DALL·E 3)

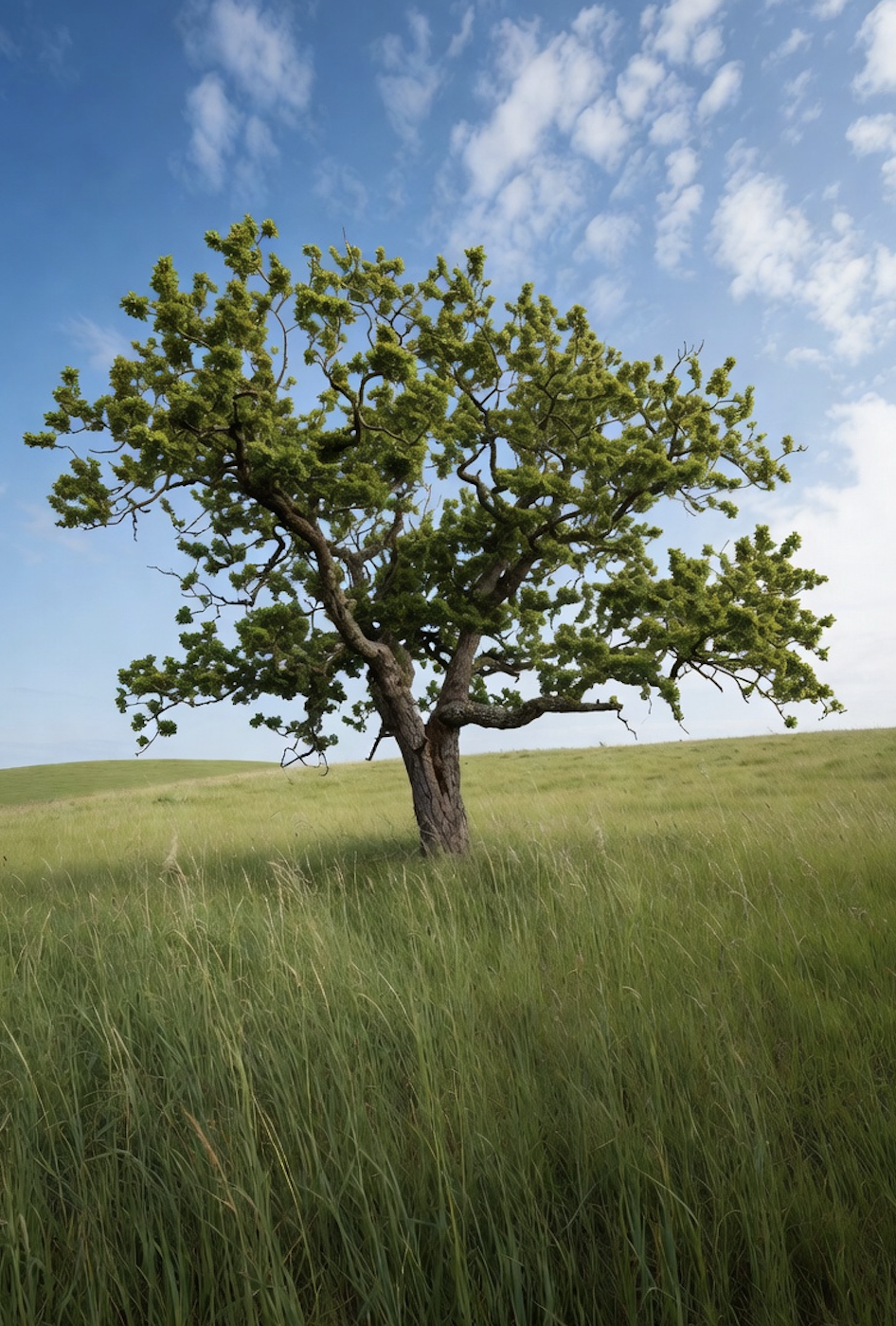
Grok Imagine

We also tested a variant of the prompt that explicitly instructed the models to avoid AI-like characteristics:
Please make sure that the image does not seem AI-generated.
However, this addition did not produce significantly different outputs. The resulting outputs can be seen here:
Control Image
To establish a baseline for comparison, we collected one authentic photograph depicting a similar scene: a mature oak tree in an open meadow. This image served as the non-AI control in our test set.

Metadata Removal
To ensure that detection platforms were evaluating visual content rather than relying on embedded metadata, we created screenshotted copies of all images. This process removed any file information, EXIF data, or obvious watermarks that could reveal the image's origin, forcing the platforms to base their assessments solely on visual characteristics.
Detection Results
Both Winston.AI and AI or Not achieved 100% accuracy in distinguishing AI-generated images from the authentic photograph. All three synthetic images (from Gemini, GPT, and Grok) were correctly identified as AI-generated, while the genuine photograph was accurately classified as authentic.
Winston.AI Performance
Winston.AI not only provided correct classifications but also displayed confidence scores for each assessment. Interestingly, the platform showed the greatest uncertainty (15% of the image being human-generated) when analysing the Grok-generated image —the image that might appear most visually unrealistic to human observers due to its implausible branching structure and uniform leaf clusters.
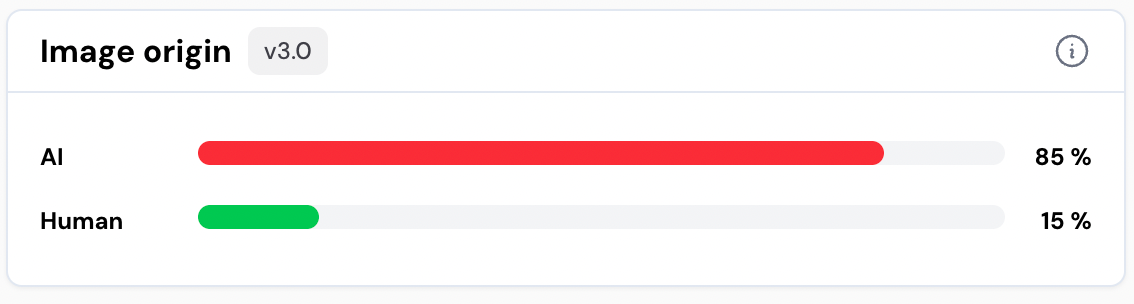
This suggests that what appears obviously synthetic to human eyes may not always trigger the highest confidence scores in algorithmic detection.
AI or Not Performance
AI or Not similarly classified all images correctly, identifying the three AI-generated images as synthetic and the authentic photograph as genuine. The platform's interface provided brief binary classifications without confidence scoring. An example output is shown here:

Recommendations
Based on our testing, both Winston.AI and AI or Not demonstrated reliable performance in detecting AI-generated images when tested on a controlled dataset. For users seeking to verify image authenticity in straightforward scenarios, either platform appears capable of providing accurate assessments.
As AI-generated content becomes increasingly difficult to distinguish visually, platforms like Winston.AI and AI or Not provide valuable verification capabilities. However, users should remain aware that detection technology exists in an ongoing arms race with generation technology—and perfect accuracy in controlled tests may not extend indefinitely to real-world scenarios.
The authors used Gemini 3 Pro (Nano Banana Pro) [Google (2025), Gemini (accessed on 14th January 2026), Image generation model, available at: https://gemini.google.com], GPT-5.2 with DALL·E 3 [OpenAI (2025), DALL·E via GPT-5.2 (accessed on 14th January 2026), Image generation model, available at: https://openai.com], and Grok Imagine [xAI (2025), Grok Imagine (accessed on 14th January 2026), Image generation model, available at: https://x.ai] to generate the images tested in this post.







